Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morita, Keisuke; Suzuki, Hideya; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Takahashi, Yuya*; Omori, Takashi*; Kaneko, Masaaki*; Asano, Kazuhito*
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.464 - 468, 2019/09
High level liquid waste (HLLW) contains several radionuclides with half-lives longer than 10 year. For reduce environmental burden of waste disposal, minor actinoids and long-lived fission products will to be partitioned and transmuted. JAEA and Toshiba developed process for recovering Se, Zr, Pd and Cs from HLLW. Solvent extraction for Zr with novel extractant,
year. For reduce environmental burden of waste disposal, minor actinoids and long-lived fission products will to be partitioned and transmuted. JAEA and Toshiba developed process for recovering Se, Zr, Pd and Cs from HLLW. Solvent extraction for Zr with novel extractant, 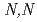 -didodecyl-2-hydroxyacetoamide (HAA) was detailed. The HAA system showed high selectivity for Zr, as indicated by the extraction order of Zr
-didodecyl-2-hydroxyacetoamide (HAA) was detailed. The HAA system showed high selectivity for Zr, as indicated by the extraction order of Zr  Mo
Mo  Pd
Pd  Ag
Ag  Sb
Sb  Sn
Sn  Lns
Lns  Fe. The extracted species was determined as Zr(HAA)
Fe. The extracted species was determined as Zr(HAA) (NO
(NO )
) (HNO
(HNO )
) . A continuous countercurrent extraction with HAA was applied to a simulated, concentrated HLLW after Pd, Se, and Cs removal, where the quantitative extraction of Zr and Mo was effectively demonstrated.
. A continuous countercurrent extraction with HAA was applied to a simulated, concentrated HLLW after Pd, Se, and Cs removal, where the quantitative extraction of Zr and Mo was effectively demonstrated.
Takahatake, Yoko; Watanabe, So; Kofuji, Hirohide; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Nomura, Kazunori; Sato, Takahiro*
International Journal of PIXE, 26(3&4), p.73 - 83, 2017/09
JAEA has been conducting research and development of MA(III) recovery from HLLW by extraction chromatography technology for reduction in amount and environmental impact of radioactive waste. The behavior of adsorbed cations inside the adsorbent packed in a column is necessary to be evaluated for improvement of the adsorbent or flow-sheet to achieve targeted MA(III) recovery performance. In this paper, micro-PIXE analysis was carried out on the particles sampled from various positions of the column to reveal the behavior of cations inside the packed column with CMPO/SiO  -P adsorbent. Simple experiment and data analysis were shown to be effective to reveal inside of the column, and formation and transportation of the adsorption bands were observed for some cations which are extractable by the CMPO extractant. Some part of Zr(IV) and Mo(VI) were found to remain inside the column without distinct transportation even after the elution operation.
-P adsorbent. Simple experiment and data analysis were shown to be effective to reveal inside of the column, and formation and transportation of the adsorption bands were observed for some cations which are extractable by the CMPO extractant. Some part of Zr(IV) and Mo(VI) were found to remain inside the column without distinct transportation even after the elution operation.
Morita, Yasuji; Yamagishi, Isao
JAEA-Research 2017-006, 27 Pages, 2017/06
Separation of Pd by extraction with 5,8-diethyl-7-hydroxy-6-dodecanone oxime (DEHDO) was examined by batch and continuous tests for the purpose of developing Pd separation process. Batch extraction tests using n-dodecane solution of DEHDO revealed that Pd, Zr and Mo were extracted from simulated high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW) and other elements were not, and also showed that the extraction rate was a little slow and a white precipitate appeared in the aqueous phase but its formation could be avoided by raising temperature. The extracted Pd was found to be back-extracted with sodium nitrite. In the continuous extraction tests with simulated HLLW without Zr and Mo, about 98% of Pd were extracted with DEHDO-n-dodecane and 95% of the extracted Pd were back-extracted with sodium nitrite and nitric acid. Continuous extraction test with simulated HLLW with Zr and Mo showed the possibility of the simultaneous separation of Pd and Mo by DEHDO extraction.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Surugaya, Naoki; Mori, Eito; Taguchi, Shigeo; Sato, Soichi
JAEA-Research 2015-013, 27 Pages, 2015/10
The H concentration generating from Highly Active Liquid Waste (HALW) of Tokai Reprocessing Plant is measured in a closed experimental system. The experimental results show that H
concentration generating from Highly Active Liquid Waste (HALW) of Tokai Reprocessing Plant is measured in a closed experimental system. The experimental results show that H concentration gradually increases at first and then approaches a steady-state due to the H
concentration gradually increases at first and then approaches a steady-state due to the H consumption reaction by Pd ions. The highest H
consumption reaction by Pd ions. The highest H concentration is 1200 ppm (0.1%) when the solution temperature is at 23
concentration is 1200 ppm (0.1%) when the solution temperature is at 23 C. It is found that H
C. It is found that H generating from HALW is equilibrated one order of magnitude lower than the H
generating from HALW is equilibrated one order of magnitude lower than the H combustion lower limit. Moreover, a model based on H
combustion lower limit. Moreover, a model based on H generation from HALW by the radiolysis and H
generation from HALW by the radiolysis and H consumption reaction by Pd ions is proposed and applied to evaluate H
consumption reaction by Pd ions is proposed and applied to evaluate H concentration behavior in the gas phase. The calculated H
concentration behavior in the gas phase. The calculated H concentrations from proposed model agreed well with the experimental values. It is demonstrated that the behavior of H
concentrations from proposed model agreed well with the experimental values. It is demonstrated that the behavior of H generating from HALW can be evaluated quantitatively by applying the proposed model in this study.
generating from HALW can be evaluated quantitatively by applying the proposed model in this study.
Committee of Handbook on Process and Chemistry of Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing
JAEA-Review 2015-002, 726 Pages, 2015/03
The fundamental data on spent nuclear fuel reprocessing and related chemistry was collected and summarized as a new edition of "Handbook on Process and Chemistry of Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing". The purpose of this handbook is contribution to development of the fuel reprocessing and fuel cycle technology for uranium fuel and mixed oxide fuel utilization. Contents in this book was discussed and reviewed by specialists of science and technology on fuel reprocessing in Japan.
Shirahashi, Koichi; Kubota, Masumitsu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 29(6), p.559 - 565, 1992/06
no abstracts in English
Ito, Tatsuya; Kim, S.-Y.*; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kimura, Takaumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Amamoto, Ippei; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Ayame, Yasuo; Utsumi, Kazuo*; Takeshita, Kenji*; Onoe, Jun*; Nagayama, Sachiko*; Hasegawa, Yoshio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Asakura, Toshihide; Tsutsui, Nao; Ban, Yasutoshi; Hotoku, Shinobu; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Morita, Yasuji; Homma, Shunji*
no journal, ,
The fundamental data on spent nuclear fuel reprocessing and related chemistry was collected and summarized as the 3rd edition of The "Handbook on Process and Chemistry of Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing". The purpose of this handbook is contribution to R&D on the spent fuel reprocessing and fuel cycle technology for high burnup uranium fuel and mixed oxide fuel utilization in near future, including minor actinides separation and recovery. Revised contents in this book was discussed and reviewed by specialists of science and technology on fuel reprocessing in Japan. In this poster presentation, the aim of the revised handbook and outline of revised data are introduced.
Kawai, Kota*; Nakano, Yoshio*; Takeshita, Kenji*; Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Amamoto, Ippei; Ayame, Yasuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Abe, Ryoji*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Pe, E.*; Abe, Ryoji*; Nagoshi, Kohei*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Amamoto, Ippei; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Ayame, Yasuo; Onishi, Takashi; Inaba, Yusuke*; Utsumi, Kazuo*; Takeshita, Kenji*; Onoe, Jun*; Koshizaka, Akiko*; Hasegawa, Yoshio*
no journal, ,
The development on synthesis of sorbent was carried out to separate the platinum group species such as Ru, Rh and Pd in high-level radioactive liquid waste. After sorption test using developed sorbents, the spherical porous silica impregnated aluminium ferrocyanide was effective to sorb the species of Ru and Pd in the nitric solution. This sorption effect remained stable when tested on actual high-level radioactive liquid waste. It was found that more treated waste could be loaded into the borosilicate glass than untreated waste.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Sato, Nobuaki*
no journal, ,
X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) analyses were performed to elucidate for simulated high level liquid waste (HLLW) and its powder samples obtained by heating up to 800 C. The purpose of this work is to elucidate chemical state of each element in the samples when the HLLW components mix with borosilicate glass. In the present work, a simulated HLLW equivalent to the HLLW stored in the JAEA Tokai Vitrification Facility (TVF) was used to evaluate the chemical state of Cr, Mn, Fe, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd and Ce elements. As the results of XAFS data analysis of cerium L
C. The purpose of this work is to elucidate chemical state of each element in the samples when the HLLW components mix with borosilicate glass. In the present work, a simulated HLLW equivalent to the HLLW stored in the JAEA Tokai Vitrification Facility (TVF) was used to evaluate the chemical state of Cr, Mn, Fe, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd and Ce elements. As the results of XAFS data analysis of cerium L -edge, it was revealed that oxidation state of cerium in the simulated HLLW was trivalent but changed to tetravalent (chemical form is CeO
-edge, it was revealed that oxidation state of cerium in the simulated HLLW was trivalent but changed to tetravalent (chemical form is CeO ) at 400
) at 400 C. The molybdate ion (MoO
C. The molybdate ion (MoO )
) , which is generally observed in the waste glass form, was found in the powder sample after heating to 500
, which is generally observed in the waste glass form, was found in the powder sample after heating to 500 C. In addition to heating temperature from 100
C. In addition to heating temperature from 100 C to 800
C to 800 C, influence of atmosphere at the heating (in air and in argon) was evaluated in the present work.
C, influence of atmosphere at the heating (in air and in argon) was evaluated in the present work.
Amamoto, Ippei; Oyama, Koichi; Nagano, Yuichi*; Jantzen, T.*; Hack, K.*; Fukayama, Daigen*
no journal, ,
As the vitrified study of the high-level radioactive waste is usually carried out under the high-temperature circumstance, it spends a lot of time and effort. The actual experiments and/or measurement, therefore, should be undertaken rationally after ascertaining the behaviors of target materials by the theoretical calculation, if possible. From such point of view, the construction of phase diagrams is considered after obtaining necessary thermodynamic properties from existing phase diagrams by CALPHAD method and/or published data. In this paper, several phase diagrams are presented such as the borosilicate glass which is currently used as the vitrified medium for the HLW, the iron-phosphate glass which will be potential vitrified medium for various wastes. Some phase diagrams are also prepared for the vitrified wastes which was loaded fission products such as molybdenum, palladium, etc..
Do, V. K.
no journal, ,
In this study, an ultra compact device for analysis of radioactive element has been developed by liquid electrode plasma optical emission spectrometry (LEP-OES) which can be possible to miniaturize the analytical equipment. The applied voltage with its sequence and nitric acid concentration are optimized and then cesium (Cs), strontium (Sr) and technetium (Tc) are measured. It is found that Cs, Sr and Tc are determined within the concentration range from ppm to ppb. Also, Cs and Sr concentration in real highly active liquid waste (HALW) are determined. The concentration of Cs and Sr in HALW agree well with the value of ORIGEN calculation. Moreover, Sr-resin from Eichrom Technology is used for solid phase extraction preconcentration and combined with LEP-OES. It is found that Sr can be preconcentration to a factor of 15 and Sr in simulated HALW are measured with the volume of 5 mL.
Yasuda, Masaki*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Arai, Yoichi; Nomura, Kazunori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Saegusa, Yu; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko
no journal, ,
Selenium-79 is a long half-life nuclide and emits low energy beta ray. Although it is difficult to analyze by radioactivity method, selenium-79 has high analytical needs for dose assessment due to the high occupancy rate of public exposure in the geological disposal of vitrified solids accompanying reprocessing of spent fuel. Selenium-79 can be measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, however, accurate analysis is difficult due to the isobaric interference. In this study, we investigated analytical method for selenium-79 by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with collision reaction cell technique. Selenium-79 can be measured after reaction with oxygen gas the cell and shift higher mass number. We will report the basic experiment results to measure selenium by collision reaction cell typed ICP-MS in this presentation.
Saegusa, Yu; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko
no journal, ,
Selenium-79 in highly active liquid waste (HAW) is important nuclides due to abundance and dose evaluation in regards to treatment and disposal of vitrified glass. Iodine-129 shifts to shearing and dissolver off-gas so it is not included in HAW. However there are few analysis report of iodine in HAW. These are difficult to be analyzed by radioactivity method due to a long half-life nuclide and emits low energy beta ray. Accurate analysis by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry is difficult due to the isobaric interference. In this study, we investigated analytical method for selenium-79 and iodine-129 by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with collision reaction cell technique. Reaction gas can be introduced into the cell and isobaric ion can be eliminated. We will report the fundamental experiment results to determine selenium-79 and iodine-129 by collision reaction cell typed ICP-MS in this presentation.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Sasage, Kenichi; Nagai, Takayuki
no journal, ,
Simulated nuclear waste glass samples were prepared by mixing and melting a simulated high level liquid waste in a phosphorus-added borosilicate glass frit. The local structure around component element in the glass was analyzed by X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) with synchrotron radiation. It was found from systematic analyses that the increase in the waste filling amount increases the oxidization property, and the increase in the phosphorus addition amount increases the reduction property and offsets these effects each another. The degree of local structural change of constituent elements due to waste loading and phosphorus addition was systematically investigated. Among these, the ratio of trivalent and tetravalent elements of cerium element changed, and the ratio of metal and oxide of rhodium element changed. With the exception of palladium, whose chemical form was found to be metal, the local structural changes in other elements were concentrated in the structural order changes of the nearest M-O pair.